Introduction
In an era of increasing urbanization and climate-related challenges, effective emergency response has never been more critical. Cities worldwide face threats ranging from natural disasters to infrastructure failures, requiring rapid, accurate, and coordinated responses. Traditional emergency response methods, while valuable, often lack the comprehensive spatial understanding needed for optimal decision-making in crisis situations.
3D city modeling and advanced surveying techniques, particularly Digital Surface Models (DSM), Digital Terrain Models (DTM), and detailed topography, are revolutionizing emergency response capabilities. These technologies provide emergency teams with critical information about terrain, infrastructure, accessibility, and environmental conditions that can mean the difference between successful response and catastrophic failure.
This article explores how 3D city modeling and surveying technologies support emergency response operations, focusing on the critical roles of DSM, DTM, and topography in navigating catastrophic events and enabling effective emergency team responses.
Understanding the Technologies
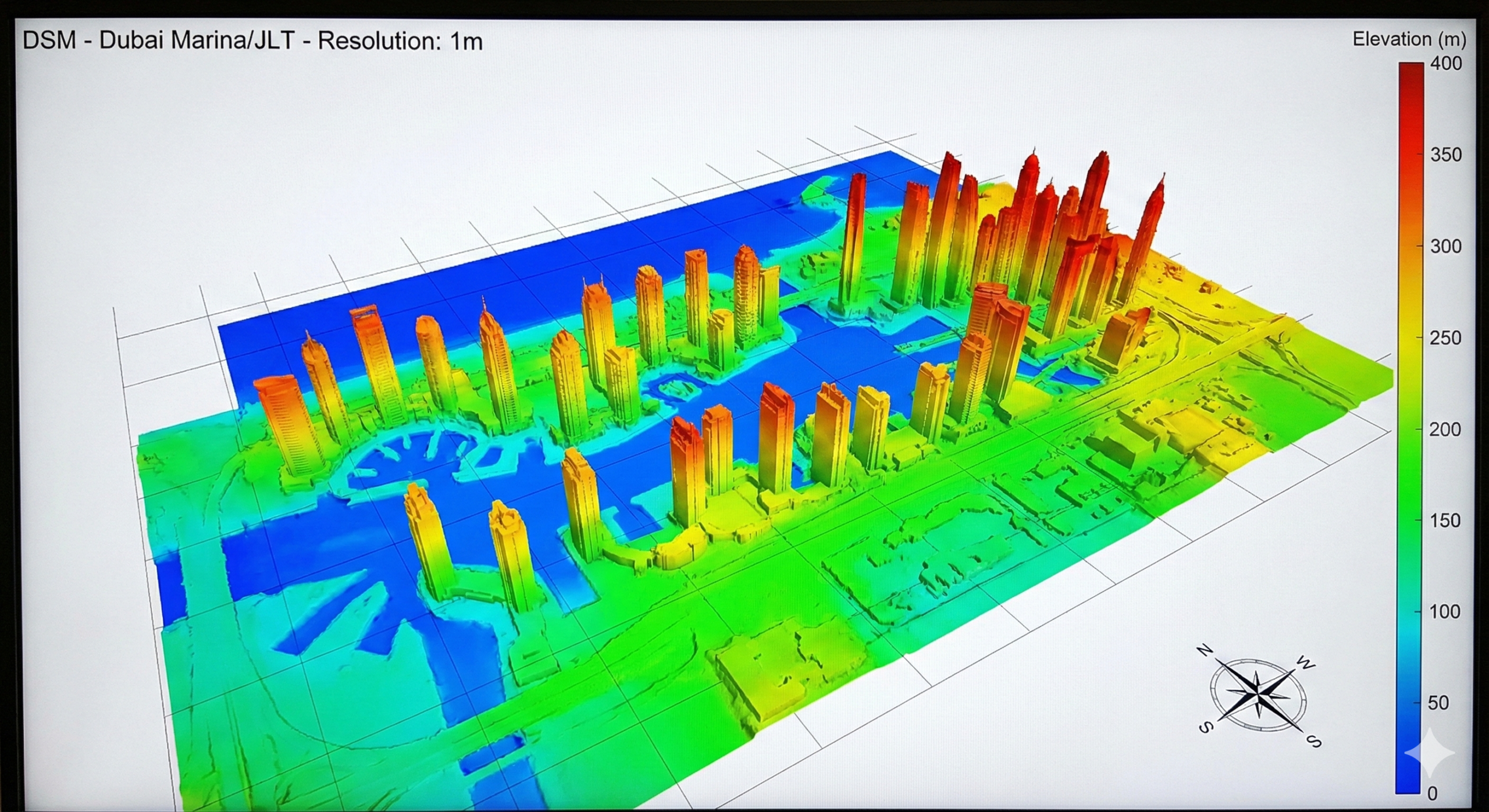
Digital Surface Models (DSM)
A Digital Surface Model represents the earth’s surface including all objects on it—buildings, vegetation, vehicles, and other structures. It provides a complete picture of the “visible” surface from above.
Key Characteristics:
- Includes all above-ground features
- Represents the “first return” from elevation data
- Captures building heights, tree canopies, and infrastructure
- Essential for understanding urban morphology
Emergency Response Applications:
- Identifying accessible routes around obstacles
- Understanding building heights for rescue operations
- Planning helicopter landing zones
- Assessing structural density for evacuation planning
Digital Terrain Models (DTM)
A Digital Terrain Model represents the bare earth surface, with all above-ground features removed. It shows the natural ground elevation and terrain characteristics.
Key Characteristics:
- Represents the actual ground surface
- Excludes buildings, vegetation, and structures
- Shows natural terrain features
- Essential for understanding topography and drainage
Emergency Response Applications:
- Planning ground-based response routes
- Understanding drainage patterns for flood response
- Identifying natural barriers and access points
- Assessing terrain for vehicle accessibility
Topography
Topography refers to the detailed mapping of surface features, including elevation, slopes, natural features, and human-made structures. It provides comprehensive understanding of the physical landscape.
Key Characteristics:
- Detailed elevation information
- Slope and gradient analysis
- Natural feature identification
- Comprehensive landscape understanding
Emergency Response Applications:
- Route planning considering terrain difficulty
- Identifying safe zones and evacuation routes
- Understanding natural barriers and advantages
- Planning resource deployment locations
The Role of 3D City Modeling in Emergency Response
Comprehensive Urban Understanding
3D city models provide emergency responders with complete understanding of:
Building Information
- Heights and Structures: Critical for rescue operations and firefighting
- Access Points: Entrances, exits, and emergency access routes
- Structural Characteristics: Materials, age, and potential vulnerabilities
- Occupancy Patterns: Understanding population density and distribution
Infrastructure Networks
- Road Networks: Understanding traffic flow and accessibility
- Utility Systems: Water, electricity, gas, and telecommunications
- Transportation Hubs: Airports, ports, and major transit points
- Critical Facilities: Hospitals, schools, government buildings
Environmental Context
- Natural Features: Rivers, hills, valleys, and coastal areas
- Vegetation: Parks, forests, and green spaces
- Climate Considerations: Wind patterns, temperature zones, and microclimates
Real-Time Situational Awareness
Modern 3D city models integrate with:
- IoT Sensors: Real-time environmental and structural monitoring
- Traffic Systems: Current road conditions and congestion
- Weather Data: Real-time meteorological information
- Social Media: Crowdsourced information about conditions
Emergency Response Applications
Flood Response and Management
DSM Applications:
- Building Elevation Analysis: Identifying structures at risk
- Water Level Prediction: Understanding potential inundation
- Evacuation Planning: Identifying safe zones above flood levels
- Rescue Operations: Planning boat and helicopter access
DTM Applications:
- Drainage Pattern Analysis: Understanding water flow directions
- Natural Channel Identification: Locating existing drainage systems
- Terrain Analysis: Identifying low-lying areas and high ground
- Infrastructure Vulnerability: Assessing critical infrastructure at risk
Topography Applications:
- Slope Analysis: Understanding water flow rates and directions
- Safe Zone Identification: Locating elevated areas for evacuation
- Access Route Planning: Identifying routes that remain accessible
- Resource Deployment: Optimal positioning of response teams and equipment
Fire Response and Management
DSM Applications:
- Building Height Analysis: Planning firefighting operations
- Vegetation Mapping: Identifying fire-prone areas
- Access Route Planning: Navigating around obstacles
- Helicopter Operations: Identifying landing and water collection zones
DTM Applications:
- Terrain-Based Fire Spread: Understanding how terrain affects fire behavior
- Natural Barriers: Identifying features that can contain fires
- Access Planning: Routes for ground-based firefighting equipment
- Evacuation Routes: Safe paths considering terrain and fire spread
Topography Applications:
- Wind Pattern Analysis: Understanding how topography affects wind and fire spread
- Slope Considerations: Steep terrain affecting fire behavior and access
- Natural Firebreaks: Topographic features that can stop fire spread
- Resource Positioning: Optimal locations for firefighting resources
Earthquake Response
DSM Applications:
- Structural Damage Assessment: Comparing pre and post-earthquake DSMs
- Debris Mapping: Identifying collapsed structures and obstacles
- Access Route Analysis: Finding navigable paths through damaged areas
- Helicopter Landing Zones: Identifying safe areas for aerial operations
DTM Applications:
- Ground Movement Analysis: Understanding terrain changes from earthquakes
- Landslide Risk Assessment: Identifying areas at risk of secondary disasters
- Access Planning: Routes that account for ground instability
- Infrastructure Assessment: Understanding how terrain changes affect infrastructure
Topography Applications:
- Seismic Risk Zones: Understanding how topography affects earthquake impact
- Evacuation Planning: Safe routes considering terrain and potential hazards
- Resource Deployment: Positioning teams in safe, accessible locations
- Recovery Planning: Understanding terrain for reconstruction planning
Search and Rescue Operations
DSM Applications:
- Visibility Analysis: Understanding line-of-sight for search operations
- Coverage Planning: Optimizing search patterns
- Obstacle Navigation: Planning routes around structures and vegetation
- Communication Planning: Optimal locations for communication equipment
DTM Applications:
- Terrain Difficulty: Understanding ground conditions for search teams
- Natural Hiding Spots: Terrain features where people might seek shelter
- Access Routes: Paths for search teams and equipment
- Resource Positioning: Optimal locations for command centers and staging areas
Topography Applications:
- Comprehensive Terrain Understanding: Complete picture for search planning
- Route Optimization: Finding most efficient search routes
- Risk Assessment: Identifying hazardous terrain features
- Team Coordination: Understanding terrain for effective team deployment
Integration with Emergency Management Systems
Command and Control Integration
3D city models integrate with:
- Emergency Operations Centers: Centralized command and control
- Dispatch Systems: Optimizing resource deployment
- Communication Networks: Coordinating multi-agency responses
- Decision Support Systems: Data-driven decision-making
Real-Time Updates
Modern systems provide:
- Live Data Integration: Real-time updates from sensors and reports
- Dynamic Modeling: Models that update as situations evolve
- Predictive Analytics: Forecasting how situations might develop
- Resource Tracking: Monitoring deployed resources and their locations
Data Collection and Processing
Drone-Based Surveying
Modern drone technology enables:
- Rapid Data Collection: Quick deployment for emergency situations
- High-Resolution Mapping: Detailed information for decision-making
- Real-Time Processing: Fast generation of models and maps
- Flexible Operations: Adapting to changing conditions
Processing Workflows
Professional processing involves:
- Photogrammetry: Creating accurate 3D models from imagery
- LiDAR Integration: Precise elevation data
- Data Fusion: Combining multiple data sources
- Quality Control: Ensuring accuracy and reliability
Case Study: Emergency Response in Urban Environments
Scenario: Major Flooding Event
Initial Assessment (DSM):
- Identify buildings at risk based on elevation
- Plan helicopter operations for rescue
- Understand urban morphology for evacuation
Terrain Analysis (DTM):
- Understand natural drainage patterns
- Identify low-lying areas requiring priority response
- Plan ground-based access routes
Comprehensive Planning (Topography):
- Integrate all factors for complete understanding
- Plan multi-modal response (ground, air, water)
- Optimize resource deployment
Best Practices for Emergency Response Modeling
Pre-Event Preparation
- Baseline Models: Maintain current 3D city models
- Regular Updates: Keep models current with urban changes
- Integration Planning: Ensure compatibility with emergency systems
- Training: Familiarize teams with model capabilities
During Events
- Rapid Updates: Quick model updates as situations evolve
- Real-Time Integration: Connect with live data sources
- Multi-Agency Coordination: Share models across organizations
- Decision Support: Use models for informed decision-making
Post-Event Analysis
- Damage Assessment: Compare pre and post-event models
- Lessons Learned: Analyze response effectiveness
- Model Updates: Incorporate lessons into future models
- Planning Improvements: Enhance future response capabilities
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
In the UAE, emergency response modeling must consider:
- Data Privacy: Protecting sensitive information
- Security Requirements: Ensuring secure data handling
- Interoperability: Compatibility with government systems
- Standards Compliance: Meeting national and international standards
Future Developments
Emerging technologies enhance capabilities:
- AI-Powered Analysis: Automated threat identification
- Predictive Modeling: Forecasting disaster impacts
- Real-Time Updates: Continuous model refreshing
- Enhanced Integration: Better connection with IoT and sensor networks
Conclusion
3D city modeling and advanced surveying techniques, particularly DSM, DTM, and topography, provide emergency response teams with critical information needed for effective crisis management. These technologies enable:
- Comprehensive Understanding: Complete picture of urban environments
- Informed Decision-Making: Data-driven response planning
- Optimized Resource Deployment: Efficient use of limited resources
- Enhanced Safety: Better protection for responders and public
For emergency services, urban planners, and government agencies in Dubai and the UAE, investing in 3D city modeling and surveying capabilities represents a critical step toward enhanced emergency preparedness and response effectiveness.
The integration of these technologies with emergency management systems creates powerful tools for protecting lives, property, and infrastructure during catastrophic events.
Ready to Enhance Emergency Response Capabilities?
At ZID – Zenith InnoDev, we combine 11+ years of engineering expertise with 4 years of specialized drone services to support emergency response planning and operations. Our 3D city modeling and surveying services provide the detailed DSM, DTM, and topographic data essential for effective emergency response.
We work with emergency services, government agencies, and infrastructure managers to create comprehensive models that support crisis management, resource planning, and response optimization.
Contact us today to discuss how 3D city modeling can enhance your emergency response capabilities.
Internal Links: